C. Work Take Home Quiz
300 Points Possible ( 10 points/question)
For
Questions #1-9, Match the unit or expression to the physical quantity.
a)
friction
bc) ft-lb
b)
J/s
ab) 1/2 mv2 bd)
-kx
c)
dyne cm
ac) dimensionless
be) weight
d)
N m
ad) N/m
cd) ftlb/s
e)
550 ftlb/s ae)
3.6 MJ
1.
joule
2.
kinetic energy
3.
potential energy
4.
conservative force
5.
non-conservative force
6.
spring constant
7.
hp
8.
Hooke's Law
9.
watt
10.
Two men, Joel and Jerry, push against a wall.
Jerry stops after 10 min, while Joel is able to push for 5 min longer.
Compare the work they do.
a. Joel does 50% more work than
Jerry.
b. Jerry does 50% more work than
Joel.
c. Joel does 75% more work than
Jerry.
d. Neither of them do any work.
11.
You lift a 10-lb physics book up in the air a distance of 1 ft, at a
constant velocity of 0.5 ft/s. The work done by gravity is
a. +10 ft-lb
b. -10 ft-lb
c. +5 ft-lb
d. -5 ft-lb
12.
The area under the curve, on a Force-position (F-x) graph, represents
a. work.
b. kinetic energy.
c. power.
d. efficiency.

13.
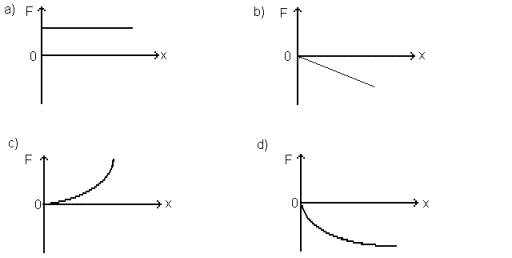
Which of the graphs illustrates Hooke's Law?
a. graph A
b. graph B
c. graph C
d. graph D
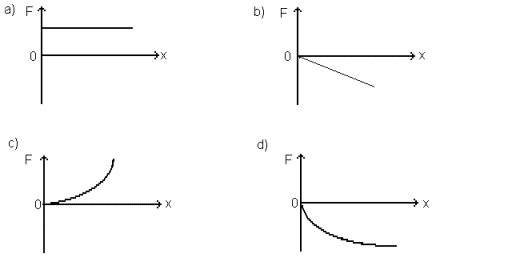
14.
Which of the above graphs represent a spring which gets less stiff the
more it is stretched?
a. graph A
b. graph B
c. graph C
d. graph D
15.
A 10-kg mass, hung onto a spring, causes the spring to stretch 2.0 cm.
The spring constant is
a. 49 N/cm
b. 5.0 N/cm
c. 0.20 N/cm
d. 0.0020 N/cm

16.
A simple pendulum, consisting of a mass m and a string, swings upward,
making an angle q with the vertical. The work
done by the tension force is: (Hint:
Ask yourself this question: “Does
the ‘bob’ move because of the tension in the string?”
If yes, then there is work done by the tension, if not, then the answer
is zero)
a. zero
b. mg
c. mg cos q
d. mg sin q
17.
Matthew pulls his little sister Sarah in a sled on a flat, icy surface
(assume no friction), with a force of 60 N at an angle of 37o upward
from the horizontal. If he pulls
her a distance of 12 m, the work he does is
a. 185 J
b. 433 J
c. 575 J
d. 720 J
18.
A container of water is lifted vertically 3 m, then returned to its
original position. If the total
weight is 30 N, how much work was done?
a. 45 J
b. 90 J
c. 180 J
d. No work was done.
19.
A truck weighs twice as much as a car, and is moving at twice the speed
of the car. Which statement is true
about the truck's kinetic energy (K) compared to that of the car?
a. All that can be said is that the
truck has more K.
b. The truck has twice the K of the
car.
c. The truck has 4 times the K of
the car.
d. The truck has 8 times the K of
the car.
20.
A toy rocket, weighing 10 N, blasts off from ground level.
At the exact top of its trajectory, its energy is 140 J.
To what vertical height does it rise?
a. 1.4 m
b. 14. m
c. 1.4 km
d. None of the above
21.
You slam on the brakes of your car in a panic, and skid a certain
distance on a straight, level road. If
you had been traveling twice as fast, what distance would the car have skidded,
under the same conditions?
a.
It would have skidded 4 times farther.
b.
It would have skidded twice as far.
c.
It would have skidded
![]() times farther.
times farther.
d.
It is impossible to tell from the information given.

22.
On the accompanying diagram of a pendulum, at what position is the
potential energy maximum?
a. A
b. B
c. C

23.
On the accompanying diagram of a pendulum, at what position is the
kinetic energy maximum?
a. A
b. B
c. C
24.
Which of the following is not a unit of work?
a. Kg-m/s
b. J
c. Kw-h
d. N-m
e. W-s
25.
If both mass and the velocity of a ball are each tripled, the kinetic
energy is increased by a factor of:
a. 3
b. 6
c. 9
d. 18
e. 27
f. 81
26.
Consider a plot of the displacement (x) vs applied force (F) for an ideal
elastic spring. The slope of the curve would be:
(Hint:
When you read this question, be sure you understand which unit is on
which axis. In other words, refer
to your knowledge of _____ vs. ______ graphs.
Which one is on the x-axis and which is on the y-axis?)
a. the spring constant
b. the reciprocal of the spring
constant
c. the acceleration of gravity
d. the reciprocal of the
acceleration of gravity
e. none of the above
27.
The work energy theorem says:
a. the net work done is equal to the
initial kinetic energy less the final energy.
b. final kinetic energy plus the net
work done is the initial kinetic energy.
c. the net work done plus the
initial kinetic energy is the final kinetic energy.
d. the net work done plus the final
kinetic energy is the initial kinetic energy.
e. the net work done minus the
initial kinetic energy is the final kinetic energy.
28.
Consider pulling a block up a frictionless ramp at some angle q. Is there any difference in
the amount of force it takes to pull the block up the ramp at a constant
velocity and the force it takes to just hold the block in place (for example:
Say you pull the block half-way up the ramp and just let the force meter
register its readings as you hold still)
a.
yes, there is a difference. The
force is greater when you pull it than when you hold it still.
b.
yes, there is a difference. The
force is lower when you pull it than when you hold it still.
c.
No, there is no difference
29. Consider the following 4 scenarios below. Which one(s) exhibit nonconservative forces (eg. A force which is affected by friction). BE CAREFUL!!! Do you understand what rolling friction is? (assume the axle on the wheeled cart is frictionless)
a.
When you are pulling a wooden block up a ramp with friction.
b.
When you are pulling a wooden block up a frictionless ramp.
c.
When you are pulling a cart on wheels up a frictionless ramp.
d.
When you are pulling a cart on wheels up a ramp with friction.
e. Both a and d are correct.
30.
What happens to the normal force on a block of wood on a ramp as you
raise the ramp to a vertical position.
a.
Normal force increases towards mg
b.
Normal force decreases towards 0
c.
Normal force doesn’t exist for carts on wheels.