
A. Static Electricity Quiz (Chapter 15)
On-Line Quiz
300 Points Possible (10 points each question)
1. A
neutral atom always has
a. more neutrons than protons.
b. more protons than electrons.
c. the same number of neutrons as
protons.
d. the same number of protons as
electrons.
2. A
glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk. During
the process the glass rod acquires a positive charge and the silk
a. acquires a positive charge also.
b. acquires a negative charge.
c. remains neutral.
d. could either be positively
charged or negatively charged. It
depends on how hard the rod was rubbed.
3. An
electron and a proton are separated by a distance of 1 m. What happens to the size of the force on the proton if the
electron is moved 0.5 m closer to the proton?
a. It increases to 4 times its
original value.
b. It increases to 2 times its
original value.
c. It decreases to one-half its
original value.
d. It decreases to one-fourth its
original value.
4. Two
charges are separated by 5.0 meters and attract one another. If one charge is halved, the other tripled, and the distance
quartered, by what factor does the attraction change?
a. 2
b. 3
c. 16
d. 24
e. 48
5. An
electron, free to move when placed in an electric field, moves
a. along the field line, opposite
the field
b. along the field line, in the
field direction
c. perpendicular to the field line
d. unaffected by the field
6. Sphere
A carries a net charge and sphere B is neutral.
They are placed near each other on an insulated table.
Which statement best describes the electrostatic force between them?
a. There is no force between them
since one is neutral.
b. There is a force of repulsion
between them.
c. There is a force of attraction
between them.
d. The force is attractive if A is
charged positively and repulsive if A is charged negatively.
7. An
electric dipole placed into a uniform electric field feels a net force:
a. along the field
b. opposite the field
c. perpendicular to the field
d. of zero magnitude

8. A
point charge of +Q is placed at the center of a square (see above diagram), and
a second point charge of -Q is placed at the upper-left corner.
It is observed that an electrostatic force of 2 N acts on the positive
charge at the center. What is the
magnitude of the force that acts on the center charge if a third charge of -Q is
placed at the lower-left corner?
a.
Zero
b.
2
![]() N
N
c.
4 N
d.
None of the above
9. An
electric dipole placed into a non-uniform electric field feels a net force:
a. parallel to the field
b. perpendicular to the field
c. of zero magnitude

10. A
point charge of +Q is placed at the centroid of an equilateral triangle (see
diagram above). When a second
charge of +Q is placed at one of the triangle's vertices, an electrostatic force
of 4 N acts on it. What is the
magnitude of the force that acts on the center charge when a third charge of +Q
is placed at one of the other vertices?
a. Zero
b. 4 N
c. 8 N
d. None of the above
11. Which
of the following makes an approximate uniform electric field?
a. a very long line of positive
charge
b. very large, closely separated,
parallel oppositely charged plates
c. two long parallel, closely
separated, oppositely charged lines of charge
d. a metal charged cylinder
12. The
electric field at the surface of a conductor is
a. parallel to the surface
b. perpendicular to the surface
c. always zero
d. never zero
13. Electric
field lines
a. are closer together the stronger
the field
b. start on negative charges and end
on positive charges
c. were invented by Isaac Newton
d. are perpendicular to the lines of
force.
14. Electric
field lines
a. circle clockwise around positive
charges.
b. circle counter-clockwise around
positive charges.
c. radiate outward from negative
charges.
d. radiate outward from positive
charges.
Page 4
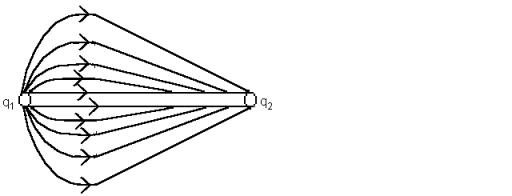
15. Two
stationary point charges q1
and q2
are shown in the sketch along with some electric field lines representing the
field between them. What can you
deduce from the sketch?
a. q1
and q2
have the same sign; the magnitudes are equal.
b. q1
and q2
have the same sign; the magnitude of q1
is greater than the magnitude of q2.
c. q1
is positive and q2
is negative; the magnitude of q1
is greater than the magnitude of q2.
d. q1
is negative and q2
is positive; the magnitudes are equal.

16. The
electric field shown
a. increases to the right.
b. increases down.
c. decreases to the right.
d. decreases down.
e. is uniform.
17. A
force of 6 N acts on a charge of 3mC
when it is placed in a uniform electric field.
What is the magnitude of this electric field?
a. 18 m
N/C
b. 2 m
N/C
c. 0.5 m
N/C
d. None of the above
18. If
a solid metal sphere and a hollow metal sphere of equal diameters are each given
the same charge, the electric field (E) midway between the sphere center and the
surface is
a. greater for the solid sphere than
for the hollow sphere.
b. greater for the hollow sphere
than for the solid sphere.
c. zero for both.
d. equal in magnitude for both, but
one is opposite in direction from the other.
19. A
hollow metallic sphere is placed in a region permeated by a uniform electric
field that is directed upward. Which
statement is correct concerning the electric field in the sphere's interior?
a. The field is zero everywhere in
the interior.
b. The field is directed upward.
c. The field is directed downward.
d. The field is zero only at the
sphere's exact center.
20. A
positive charge is enclosed in a hollow metallic sphere that is not grounded.
At a point directly above the hollow sphere, the electric field caused by
the enclosed positive charge has
a. diminished to zero.
b. diminished somewhat.
c. increased somewhat.
d. not changed.
21. A
positive point charge is enclosed in a hollow metallic sphere that is grounded.
At a point directly above the hollow sphere, the electric field caused by
the enclosed positive charge has
a. diminished to zero.
b. diminished somewhat.
c. increased somewhat.
d. not changed.
22. Which
of the following is a vector?
a. Electric constant k
b. Electric charge
c. Electric field
d. All of the above
23. Several
electrons are placed on a hollow metal sphere.
They
a. clump together on the sphere's
outer surface.
b. clump together on the sphere's
inner surface.
c. become uniformly distributed on
the sphere's outer surface.
d. become uniformly distributed on
the sphere's inner surface.
24. Electric
Dipoles always consist of two charges that are
a. equal in magnitude; opposite in
sign.
b. equal in magnitude; both are
negative.
c. equal in magnitude; both are
positive.
d. unequal in magnitude; opposite in
sign.
25. In
electricity, what quantity is analogous to the "acceleration of
gravity" g (which is a force per unit mass):
a. electric force
b. electric field
c. electric potential
d. electric charge
26. The
force which binds, or holds, atoms together to form molecules is
a. magnetic
b. electrical
c. gravitational
d. nuclear
e. friction
27. When
an electron is removed from a neutral atom, it becomes:
a. a positive ion
b. a negative ion
c. a bipolar atom
d. heavier
e. none of the above
28. The
electric constant (k in kqQ/r2)
is
a. negative for negative charge
b. positive for all charges
c. equals 1 in SI units
d. positive only for positive charge
29. Which
is true?
a. unlike charges repel
b. like charges attract
c. all charges attract
d. unlikes attract
30. Avogadro's
number of protons is contained in a
a. nucleus
b. mole
c. neutral atom